For many people, oral care is all about their teeth, which they want to keep clean and shiny white, or about their breath, which they worry isn’t fresh. Gums can, unfortunately, be an afterthought, but they play a vital role by acting as a barrier against bacteria that causes disease, while also supporting your teeth to keep them in place.
Gum recession refers to the gums pulling back from the surface of the tooth, exposing the roots. This is a common condition, but one that can be avoided with appropriate care. Unfortunately, many do not realize that their gums are receding until the condition has advanced to a later stage.

Symptoms of Gum Recession
Receding gums are most often seen in adults over the age of 40 and are more common in men than women, though it is worth knowing and watching for the signs to catch it early, regardless of age or gender. Receding gums and other forms of periodontal disease will be diagnosed by your dentist, but some of the indications that you may experience include:
- Bad breath
- Bleeding after brushing or flossing
- Swollen red gums
- Pain at the gum line
- Visibly shrinking gums
- Exposed roots
- Loose teeth
Causes of Gum Recession
There are several factors that could lead to receding gums. Poor oral health is one possibility. If plaque is allowed to build on the gums and teeth, this can lead to the gums becoming inflamed. If this inflammation remains untreated, it can result in the deterioration of the gums and supporting bone structure. Other potential causes include:
Overly Aggressive Brushing
It might seem as though vigorous brushing is a good way to get your teeth their cleanest, but it can be harmful by wearing down the enamel of your teeth and causing damage to your gums.
Genetics
If one or both of your parents suffer from gum recession, you may be at a higher risk.
Tooth Position
If your teeth are not aligned properly, it can create friction that results in your gums receding.
Clenching or Grinding Your Teeth
Along with causing other issues, clenching, or grinding your teeth can exert a force that wears down your gums much like misaligned teeth.
Trauma to Gum Tissue
Gum recession can occur at the site of a gum injury or nearby.
Tobacco Use
Smoking and other forms of tobacco use increase the risk of receding gums by causing other issues such as inhibited saliva flow and weakening the immune system.
Hormonal Changes
Women can be more susceptible to receding gums as they experience hormonal changes brought about by puberty, pregnancy, and menopause.
Gum Recession Treatment
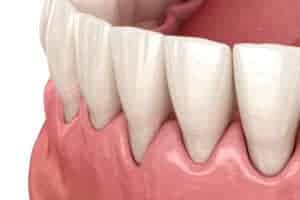
In mild cases of gum recession, treatment is usually not required. Your dentist may offer tips on prevention and continue to monitor your gums. A proper brushing technique that is not too aggressive is an effective intervention.
If treatment is required, there are several options:
Desensitizing Agents and Dentin Bonding Agents
These are ways to reduce the sensitivity of exposed roots. They can make brushing sensitive teeth more comfortable.
Pink Porcelain or Composite
This is a material that matches the colour of the gums and is used to fill in the space where gums have receded.
Removable Gum Veneers
These are used to replace large areas of missing gum tissue and are usually made of acrylic or silicone.
Orthodontics or Invisalign
Moving the teeth slowly over a lengthy period can correct the gum margin and make it easier to keep the teeth clean.
Surgery
This requires grafting tissue from another site in the mouth which heals over the recessed area. This is an option for severely receded gums.
Gum tissue unfortunately does not grow back, making it important to ensure that your oral care routine takes gum care into consideration. Proper brushing and flossing can go a long way toward protecting your gums and keeping them healthy.


0 comments on “Gum Recession: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment”